The transcription factor Bcl11b: a new regulator of canonical and non-canonical NF-kB pathways
Abstract:
Background: Bcl11b, a zinc finger bi-functional transcription factor, is highly expressed in various tissues during development and differentiation such as skin and immune system. The canonical and non-canonical NF-kB pathways are known in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases that can be activated by cytokine stimulation. However, the mechanism of cytokine activation and regulation of Bcl11b in relation to the NF-kB pathways is not completely understood.
Objective: To investigate the role of Bcl11b in the regulation of NF-kB pathways in keratinocytes as an example of psoriasis.
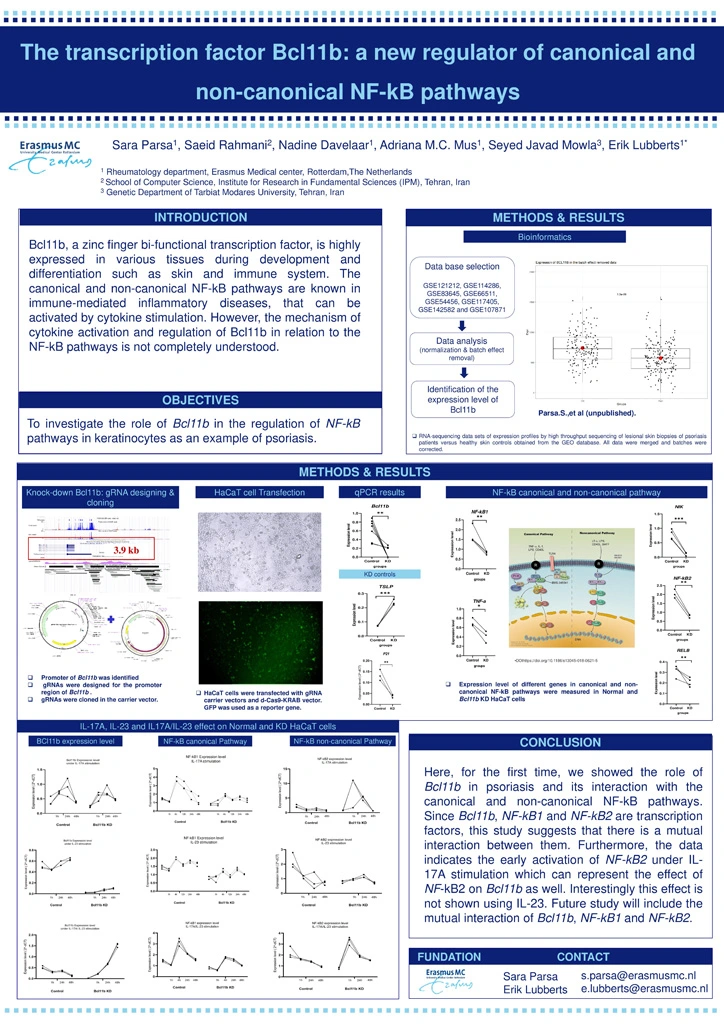
Methods: Online data sets of psoriatic and healthy skin samples were downloaded in order to examine the expression level of Bcl11b in an in silico analysis using R programing. HaCaT keratinocytes were cultured and Bcl11b were knocked down in these cells using the CRISPR/Cas9 approach. qPCR was performed to analyze the expression level of Bcl11b, control genes and NF-kB pathway genes. In addition, the effect of IL-17A, IL-23 and IL-17/IL-23 activation on the canonical and non-canonical NF-kB pathways in HaCaT keratinocytes was investigated in the presence or absence of Bcl11b.
Results: Bioinformatic analysis of online data sets indicated a down regulation of Bcl11b among psoriasis skin biopsies compared to healthy skin controls. Given this, Bcl11b were knocked down in keratinocytes which was confirmed using q-PCR for Bcl11b as well as TSLP and P21 as controls. Expression analysis of NF-kB pathway genes including NF-kB1, TNF-a, NF-kB2, RELB and NIK indicated an upstream role of Bcl11b in both the canonical and non-canonical NF-kB pathways. We therefore further analyzed these pathways under inflammatory conditions. Cytokine stimulation showed that IL-17A can return the Bcl11b expression level to normal in Bcl11b knocked down keratinocytes, in contrast to IL-23. However, there was a much stronger effect using both cytokines together. Interestingly, IL-17A, in contrast to IL-23, also activated the non-canonical NF-kB pathway in the knockdown keratinocytes even more than under normal condition.
Conclusions: Here, for the first time, we showed the role of Bcl11b in psoriasis and its interaction with the canonical and non-canonical NF-kB pathways. Since Bcl11b, NF-kB1 and NF-kB2 are transcription factors, this study suggests that there is a mutual interaction between them. Furthermore, the data indicates the early activation of NF-kB2 under IL-17A stimulation which can represent the effect of NF-kB2 on Bcl11b as well. Interestingly this effect is not shown using IL-23. Future study will include the mutual interaction of Bcl11b, NF-kB1 and NF-kB2.