Biologic and Targeted Synthetic Therapies in Psoriatic Arthritis and the Risk of Opportunistic Infections
Background: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic, immune-mediated disease with genetic and environmental components to pathogenesis. In Canada, the prevalence is estimated at 0.45%. Secukinumab (Sec), an IL-17A antagonist, is a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD) that has shown safety and efficacy in treatment of PsA and has been available in Canada since 2015. T-helper-17 (Th17) cells, mast cells, and neutrophils release the proinflammatory cytokine, IL-17. Secukinumab selectively binds to the IL-17A cytokine, inhibiting its interaction with the IL-17 receptor. Phenotypic manifestations of PsA have been associated with specific HLA alleles1,2. HLA susceptibility alleles select different T cell repertoires, activating different immune effector pathways with variable response to a range of biologics1-4. It is known that HLA B27 is associated with spondyloarthritis1-4.
Objective: The primary aim of the study was to determine whether HLA class I profiles had an association with retention to treatment with secukinumab. A secondary objective was to determine the percentage of patients remaining on Sec for up to 3 years and predictors of drug retention.
Methods: Data was collected prospectively and analyzed retrospectively from a Newfoundland PsA cohort started in 2007. Patients were indexed on the date they first initiated secukinumab. Retention was assessed at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months using clinical and laboratory data including TJC28, SJC28, health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), patient and physician global assessments, PASI scores, and CRP. Serologic HLA class I typing was performed. IBM SPSS v.29.0 was used to calculate Kaplan-Meier survival curves and 2-tailed Spearman correlation coefficients.
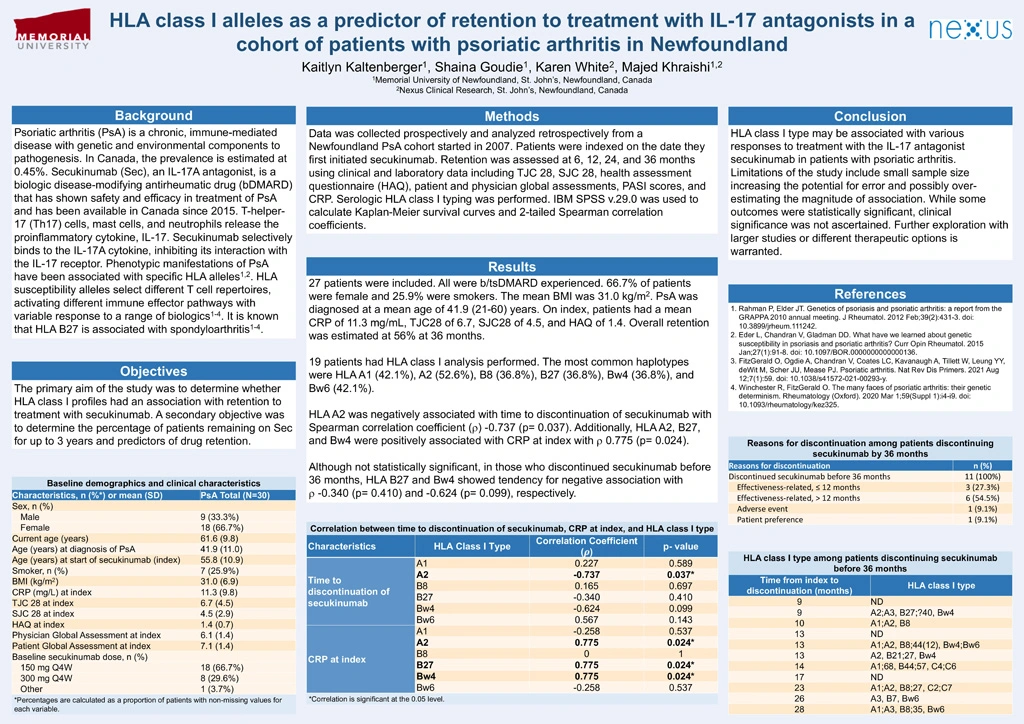
Results: 27 patients were included. All were b/tsDMARD experienced. 66.7% of patients were female and 25.9% were smokers. The mean BMI was 31.0 kg/m2. PsA was diagnosed at a mean age of 41.9 (21-60) years. On index, patients had a mean CRP of 11.3 mg/mL, TJC28 of 6.7, SJC28 of 4.5, and HAQ of 1.4. Overall retention was estimated at 56% at 36 months.
19 patients had HLA class I analysis performed. The most common haplotypes were HLA A1 (42.1%), A2 (52.6%), B8 (36.8%), B27 (36.8%), Bw4 (36.8%), and Bw6 (42.1%).
HLA A2 was negatively associated with time to discontinuation of secukinumab with Spearman correlation coefficient (r) -0.737 (p= 0.037). Additionally, HLA A2, B27, and Bw4 were positively associated with CRP at index with r 0.775 (p= 0.024).
Although not statistically significant, in those who discontinued secukinumab before 36 months, HLA B27 and Bw4 showed tendency for negative association with r -0.340 (p= 0.410) and -0.624 (p= 0.099), respectively.
Conclusion: HLA class I type may be associated with various responses to treatment with the IL-17 antagonist, secukinumab, in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Limitations of the study include small sample size increasing the potential for error and possibly over-estimating the magnitude of association. While some outcomes were statistically significant, clinical significance was not ascertained. Further exploration with larger studies or different therapeutic options is warranted.
References:
- Rahman P, Elder JT. Genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a report from the GRAPPA 2010 annual meeting. J Rheumatol. 2012 Feb;39(2):431-3. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111242.
- Eder L, Chandran V, Gladman DD. What have we learned about genetic susceptibility in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;27(1):91-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000136.
- FitzGerald O, Ogdie A, Chandran V, Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Tillett W, Leung YY, deWit M, Scher JU, Mease PJ. Psoriatic arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Aug 12;7(1):59. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00293-y.
- Winchester R, FitzGerald O. The many faces of psoriatic arthritis: their genetic determinism. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Mar 1;59(Suppl 1):i4-i9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez325.